What curious alchemy is hidden behind the complicated name "Metallurgy of powders"?
To short, it is the most recent technology for the production of metal alloys that is performed by sintering unlike the traditional fusion.
We are well advanced ... What is "sintering"?
Sintering is an ancestral method of manufacturing usual objects of heating a powder without bringing it to the melting and whose best known example is ... the pottery. Powder metallurgy is therefore the technology of developing alloys of steels by the sintering method. You understood it, the most modern and the most efficient steels are obtained according to a discovery technique, probably by chance, by the first men.
But everything is not so simple ...
Back on the history of steel design ...
If the first men were content with a mixture of earth, clay, a little water and fire to create pottery and figurines, it does not do the same for the development of steel alloys.
From the beginning of the iron age to the Middle Ages, the bottom furnaces were used to obtain iron by the merger of ore. Then, from the Middle Ages, the blast furnaces allowed to obtain melting, which can be used in the manufacture of iron alloys we know.
Even today, alloys are produced by the melting of a basic metal element mixed to one or more other so-called "alloy elements". The proportion of each of the elements of this combination determines the characteristics and properties of the steel obtained.
The beginnings of the steels designed by powders metallurgy:
From the beginning of the 1960s, the metallurgical industry was interested in the sintering technique to produce steel with improved skills (better machinability, forging, mechanical strength ...)
The use of this technology makes it the most recent process of production of steels but also the most efficient, allowing both to obtain steels with improved capacities but also simply to obtain new alloys and special steels that it would be impossible to achieve by a conventional merger process.
Steel manufacturing steps by powder metallurgy
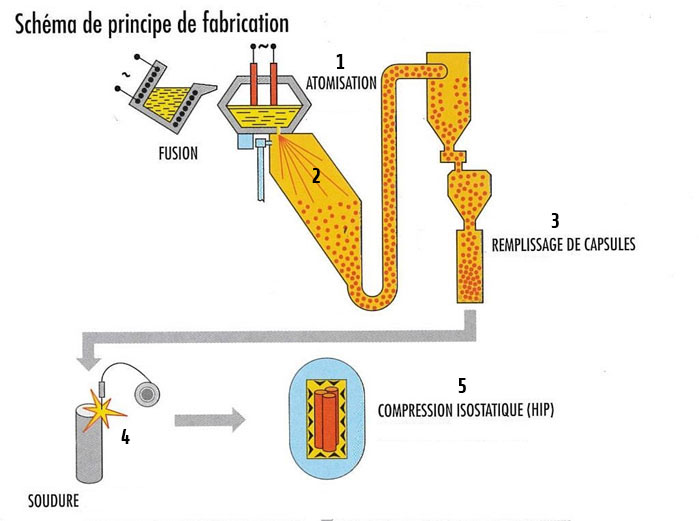
As the name suggests, powder metallurgy is a perfectly controlled and automated process based on the use of metal powders. The raw materials are dumped into a receptacle in proportions corresponding to the alloy to be developed.
- The contents of the tank is brought to its melting point by graphite electrodes and strack permanently by means of electromagnets (1)
- when the mixture is perfectly homogeneous, the alloy in its liquid phase flows into a chamber where it is subjected to an atomization process (2) By a powerful neutral gas jet (eg argon or nitrogen) that will have the effect of transforming the metal to the liquid state in micro droplets cools quickly. The powders thus obtained are perfectly homogeneous and free of impurities (or inclusions). The ideally spherical form and the size of the grains (from 0.1 to 1000 μm) are determined very precisely according to the nature of the desired alloy.
- Once these powders obtained, they are collected in a capsule (3)
- after having been closed hermetically by welding (4)it is transferred to a hot isostatic compression oven (HIP: Hot Isostatic Pressure). During this stage, the powders will compress (5) and agglomerate to form a steel billet, free from impurity or inclusion.
The assets of powder metallurgy for cutlery steel
Steels from powder technology benefit from extremely fine and regular grain, which allows them to combine benefits:
- Excellent cutting edge
- Easy sharpening and sharpening
- Enhanced polishing ability
- Improved corrosion resistance
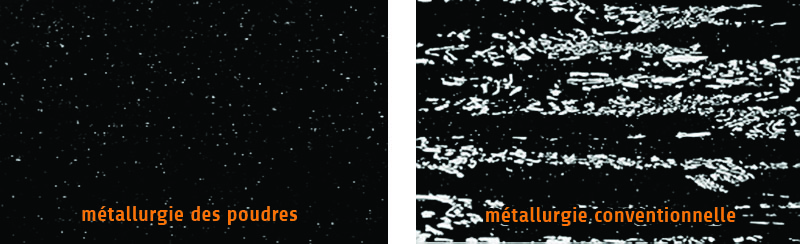
- Perfect homogeneity of steels: Best carbide distribution
- Very high purity (absence of inclusions)
- High tenacity (resistance capacity for crack propagation)
- And many others!
Many steels benefiting from this technology are available on our online store!
Difference of carbide distribution between metallurgy of conventional metallurgy powders: